
The blood sugar values indicate the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Blood sugar is important for human health because it is a source of energy for the cells and thus for the whole body. The levels are affected by a variety of factors, including dietary consumption, and can change during the day. To prevent diseases, it is advisable to have the values checked at regular intervals in order to be able to treat diseases such as diabetes at an early stage. In this article, you will find important information about blood sugar values: the meaning of the various values and the normal values in adults and children.
What are blood sugar levels?
Blood sugar values describe the sugar content in the blood. This changes constantly during the day due to food intake and it is completely normal for the value to fluctuate. The values are lowest in the morning because you did not eat any food during the night and the values rise after eating.
Blood sugar is responsible for the energy supply of the cells. Glucose is absorbed with food and enters the blood from the intestines. Glucose is carried into cells in the blood by insulin, a hormone generated in the pancreas, and absorbed there. Some diseases affect the regulation of blood sugar levels. It's predictable that your pancreas isn't producing enough insulin. The person concerned then suffers from diabetes mellitus.
Read this too How to cure diabetes in 8 weeks
A distinction is made between two measurement data for the measured values: the short-term sugar and the long-term sugar. If a routine examination is carried out, the short-term sugar, which indicates the day-dependent fluctuations in the glucose value, is examined. With this value, diabetics can tell whether they are about to have hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia and can thus avoid a sugar shock. Long-term sugar levels, on the other hand, are checked every two to three months. In the treatment of diabetes, the value can be particularly helpful in making prognoses.
HbA1c value
The HbA1c value, also known as glycosylated hemoglobin, plays an important role in assessing blood sugar control. This number denotes the percentage of “sugared” red blood pigment in total hemoglobin. HbA1c does not only develop in diabetics, but in every human being. The value is based on the average blood sugar concentration - in other words, the higher the blood sugar level is over a longer period of time, the higher the HbA1c value. This number may be used to calculate blood sugar levels for the previous 8 to 10 weeks. In addition to the blood sugar measurement and the glucose tolerance test, both of which are explained in the following sections, the test of the HbA1c value is extremely important in diabetes therapy.
Read this How to reduce high blood sugarHow is blood sugar measured?
Blood glucose is measured in the laboratory or using portable blood glucose meters. This can be done by a doctor, medical staff, or the patient himself (after detailed instruction). Since the blood sugar level can fluctuate widely throughout the day, a single test is not sufficient. Therefore, several measurements have to be made for a longer period of time so that it is certain whether the blood sugar values are permanently too high or too low.
The blood sugar measurement takes place in the fasting state of the patient. In this context, fasting means before the patient has consumed food. The end outcome is known as fasting blood sugar. One pricks the finger or the earlobe lightly so that a small drop of blood can be obtained. This drop is placed on a tiny stick, which is then put into a blood glucose meter. After about 30 seconds, the device displays the sugar content of the blood is examined. The value can also be determined with a normal blood sample.
Detailed and further information on this topic can be found in the article Measuring blood sugar.
Unit of measurement for blood glucose measurement
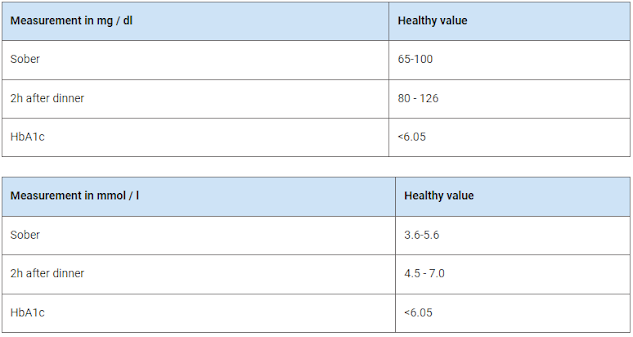
The blood sugar value can be specified in two units of measurement: "Millimoles per liter" (mmol / l) or "Milligrams per deciliter" (mg/dl). In western Germany, it is common to give the values in milligrams per deciliter, i.e. mg/dl, and in eastern Germany the internationally recognized unit of measurement, millimole per liter, i.e. mmol / l is used. While mg/dl indicates the weight of the dissolved sugar particles per volume, the unit of measurement is mmol / l to indicate the number of particles, i.e. the amount of substance, per volume. It is also important to mention that deviating standard values often appear in the specialist literature.
Oral glucose tolerance test (oGBT)
The oral glucose tolerance test is another measurement (sugar load test). This indicates whether there is a glucose tolerance disorder and is therefore used to diagnose diabetes. At the beginning of the examination, the fasting blood sugar level is determined. Then the patient drinks a precisely measured amount of sugar solution. Two hours later, it is measured how high the blood sugar level has risen and how quickly it falls again. If the values are clearly elevated, this indicates diabetes. However, there are also patients who have abnormal sugar levels but have not yet developed diabetes. This is then a preliminary stage of diabetes.
Read this what is insulin resistance
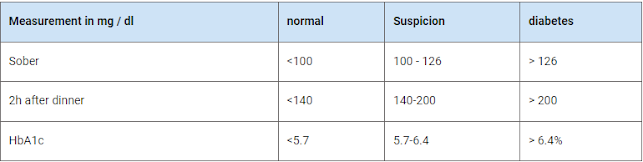
Normal blood sugar levels (table)
Normal blood sugar levels are measured on an empty stomach. Sober means that you have not eaten anything before the test, which is the case, for example, in the morning right after you get up. A total of 8 hours beforehand, nothing may be eaten and only water may be drunk.
The normal fasting blood sugar values for adults are between 60-100 mg/dl (milligrams per deciliter) or between 3.3-5.6 mmol / l (millimoles per liter). After eating, the blood sugar levels rise and are between 90 - 140 mg/dl or 5.0 - 7.8 mmol / l.
Blood sugar levels in adults
The following tables show the normal blood sugar values in adults as an overview:

Blood sugar levels children
Children have a different blood sugar normal value than adults and there are also age-dependent differences in the normal values among children. In a 1-day-old infant, the values are between 34 and 99 mg/dl, and from the 2nd day of life, the value is between 46 and 81 mg/dl. Thereafter, the same healthy value applies to children, which can be found in the tables.
Blood sugar levels in the oral glucose tolerance test.
HbA1c levels
This table provides an additional overview of the relationship between the HbA1c values in the various units of measurement. The HbA1c value describes the average sugar content over the past 8 to 10 weeks. The normal value for a healthy person is 5 to 6%, for a well-adjusted diabetic it is 6 to 7% - if the value exceeds this, a diabetic is described as poorly adjusted. Since several factors, such as age and personal constitution, have an influence on the value, the percentage is never 100% certain.
Conversion tables for blood sugar values
The following formulas are used to convert the values into the other unit of measurement:
mg / dl x 0.0555 = mmol / l
mmol / lx 18.02 = mg / dl
As the numbers are rounded after the decimal point, there may be slight inaccuracies. There are also tables that can provide a quick overview.
Which blood sugar levels are too high?
The fasted blood sugar level is too high if it is above ≥ 110 mg/dl or 6.1 mmol / l. Then there is a suspicion of diabetes. After eating, the blood sugar values of 140 mg/dl or 7.8 mmol / l are too high, which indicates, for example, a disturbed glucose tolerance.
Reasons for values that are too high include the following:
- Diabetes, diabetes mellitus
- Diabetes during pregnancy
- Hormonal disorders caused by tumors in the adrenal medulla
- Hormonal disorders caused by tumors of the pituitary gland
- Pancreatic disease
- Hereditary diseases
- A side effect of certain drugs
If the blood sugar level is increased, symptoms such as a feeling of thirst, increased urination and visual disturbances occur. If it is extremely high, there is a risk of a life-threatening coma and, in the long term, too high a value will damage the blood vessels. This can result in atherosclerosis, stroke, kidney failure, and loss of vision. This can also lead to tissue damage, for example on the lower legs and feet.
Which blood sugar levels are too low?
If the blood sugar level is less than 70 mg/dl or 3.9 mmol/l, it is considered too low. Too low blood sugar manifests itself in the beginning by hunger, dizziness, tiredness, and sweating. If the value is not changed, i.e. no sugar is added, seizures, circulatory collapse, shock, and even death can result.
- If the blood sugar level is too low, this can have the following causes:
- Insulin overdose during diabetes therapy
- Overproduction of insulin caused by tumors in the pancreas
- Disorders of the hormonal balance
- Excessive physical work and poor food intake
- Malnutrition due to alcohol, fasting, or refusal to eat
- Severe liver damage, such as cirrhosis of the liver
- Drinking alcohol on an empty stomach
If people have been suffering from diabetes for a long time, it is possible that hypoglycemia will not be symptomatic. There are few or no symptoms, which is why there is no timely response. That is why diabetics have to check their blood sugar levels. Especially if you are very physically active and do a lot of sport.
How can you lower blood sugar?
There are various ways to reduce high blood sugar levels. Even an adapted diet with reduced sugar content and an increase in fiber in combination with exercise can lower the blood sugar level. The increasing movement supports muscle work and requires more energy, which is supplied by glucose in the blood. Medicines can also be used to help lower blood sugar levels. Special drugs for diabetics are called antidiabetic drugs. With the help of insulin syringes, diabetics can quickly influence their blood sugar levels.

















0 Comments